This is a practical guide on how to use Realm in a SwiftUI project.
For this tutorial I will be using a Local Realm database.
Install
Using SPM install the SDK: https://github.com/realm/realm-swift.git and select both Realm and RealmSwift.
You can import it into your project with import RealmSwift
Let's take a look now at the basic CRUD functions:
Define model
You can find all the supported data types on the official docs.
To approach this I'll use the typical to-do list example. Create a model with the following:
import Foundation
import RealmSwift
class ToDo: Object, ObjectKeyIdentifiable {
@Persisted(primaryKey: true) var id: ObjectId
@Persisted var name: String
@Persisted var completed = false
@Persisted var urgency: Urgency = .neutral
enum Urgency: Int, PersistableEnum {
case trivial, neutral, urgent
var text: String {
switch self {
case .trivial:
return "Trivial"
case .neutral:
return "Neutral"
case .urgent:
return "Urgent"
}
}
}
convenience init(name: String) {
self.init()
self.name = name
}
}Explanation:
In Realm you define your model classes by subclassing Object and adding properties to be managed. You then instantiate and use your custom subclasses instead of using the Object class directly.
The @Persisted property wrapper is managed by Realm and will allow us to persist the data. We also add a unique key to our model by adding @Persisted(primaryKey: true)
Create
Think of creating new objects as adding rows to a database, every time you create a new object you add a new row to the local DB, in our Swift example it would be adding new items to an array, so you append them. First, access the Observer on our view:
@ObservedResults(ToDo.self) var toDosthen you can create the object like this:
let newToDo = ToDo(name: name)
$toDos.append(newToDo)Read
To read the model you just created you can use @ObservedResults(ToDo.self) var toDos, the brilliant thing about this is that we can use it in our view as if we were using a SwiftUI environment, very handy:
List() {
ForEach(toDos) { toDo in
Text(toDo.name)
}
.listRowSeparator(.hidden)
}
.listStyle(.plain)Using Realm Studio - optional
Realm Studio is a visual tool to view, edit, and design Realm Database files. Download link.
After you download the app, on the @main view, create an .onAppear like so to find the path of the realm objects:
.onAppear {
print(FileManager.default.urls(for: .documentDirectory, in: .userDomainMask).first!.path)
}Next, relunch the app and go to the path printed on the console (if you didn't create any entry on the db yet then the dir. will be empty). If you have some items, you'll see a file called default.realm, you can open it with realm studio. It looks like this:
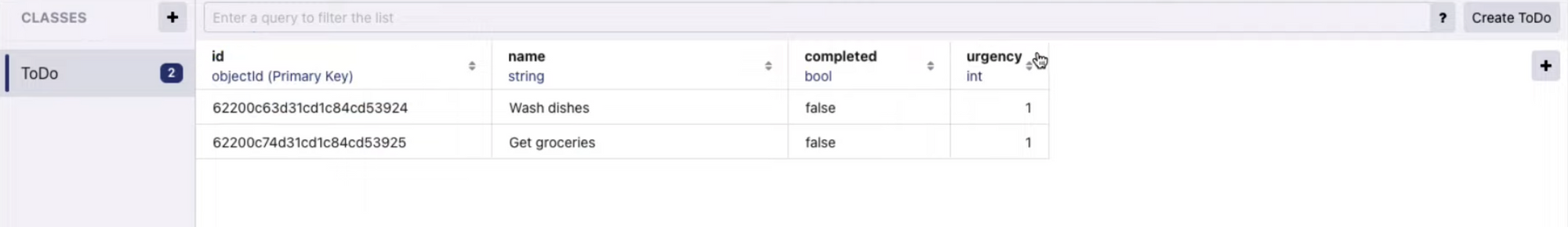
If you edit the data while running the simulator, you can see the changes in real time.
Update
To update the value of 1 object using @ObservedRealmObject var toDo: ToDo you can use:
$toDo.completed.wrappedValue.toggle()Delete
You can delete an item inside a ForEach by pointing to it with:
$toDo.delete()Possible errors
- The SwiftUI View is not updating the state once you update Realm objects
This happens because you updated the object, but the previous view has no clue what you did. What you have to do is make sure both views data are linked by Binding the Realm objects, so if you add a new view, make sure you do something like: AddNewToDo(toDo: $toDo)
2. If you get something like below is because you are trying to update the Realm object that is frozen. It's very likely you used @ObservedResults instead of @ObservedRealmObject to update that object. Also make sure you have the $ at the beggining of your update line, check above how I did the Update for reference.
Thread 1: "Attempting to modify a frozen object - call thaw on the Object instance first."The above would "fix" it when you are modifying 1 object, however if you want to modify other objects that are not the one in the current view, you'll get something similar. For that, you need to thaw the object, ex: .thaw()?.name = ""
See for more info on thawing here & here.
Special thanks to: Realm, Stewart -> sourcecode


